does autoclaving kill non-enveloped viruses|viruses with envelope on surface : ODM Understanding the molecular basis of the penetration mechanisms of non-enveloped viruses is a prerequisite for therapeutic target identification and may pave the way .
So today I would like to demonstrate how to sterilize dental instruments using the Midmark autoclave. It is the biggest sterilizer in the dental office, but very simple to use if used properly. .
{plog:ftitle_list}
The autoclave test does not correctly predict the long-term expansion of cements. Slag cements were effective in reducing the ASTM C151 autoclave expansion. Increasing the .While it’s not a substitute for sterility assurance testing, the Bowie-Dick test cycle demonstrates proper air removal from the chamber of a pre-vacuum autoclave. Pockets of cool air can form inside the chamber of a pre-vacuum autoclave, acting as a barrier that prevents steam from penetrating and sterilizing the . See more
viruses with no envelope
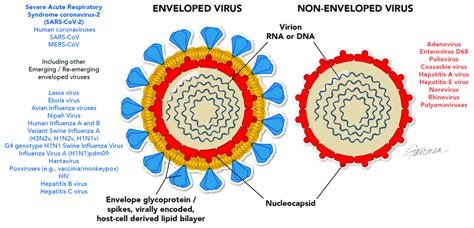
Envelope. • Phospholipids acquired from the host aid in evasion of the immune system. • Sensitive to chemical and physical treatments like ethanol, bleach, heat, and UV. Examples. • Influenza virus and SARS-CoV-2 are enveloped viruses. • Norovirus and hepatitis A virus are .Is it a bacteria, virus, fungus, or protozoa? Does it form fungal or bacterial spores? If it’s a virus, is it enveloped or non-enveloped? Pure cultures are easy to identify, but for animal, human, or .
viruses with envelopes
The distinct effects of the chemical treatment on the morphology of HAdV5 and FCV suggests that non-enveloped viruses with icosahedral geometry can follow different .
The ability of autoclaving to degrade viral genomes was investigated by real-time PCR and real-time reverse-transcription (RT)-PCR. Several factors were considered: the nucleic acid .
Our study unexpectedly found that commercialized DNB was highly effective in inactivating SARS-CoV-2 at very low concentrations, inactivating the virus in 0.5 min after .
Understanding the molecular basis of the penetration mechanisms of non-enveloped viruses is a prerequisite for therapeutic target identification and may pave the way .
How do viruses spread from cell to cell? Enveloped viruses acquire their surrounding membranes by budding. If a newly enveloped virus has budded through the plasma membrane, it finds .As SARS-CoV-2 is an enveloped virus easily susceptible to disinfection, as verified in the review findings, methods that can effectively target more resilient surrogate enveloped viruses .
Non-enveloped viruses, echovirus type 11 and reovirus type 3 have been also tested but seemed unaffected by the action of defensins.
viruses with envelope problems
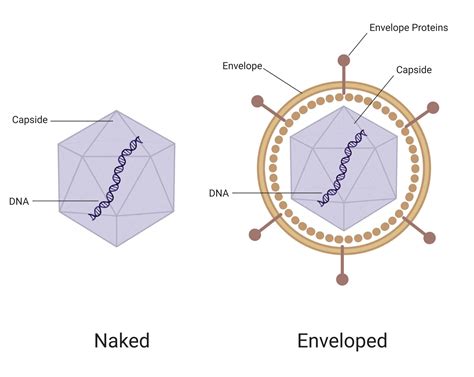
One of the major and best-known virus classifications is the separation of enveloped from non-enveloped viruses. In general, what distinguishes them is the presence .Non-enveloped viruses. contain no lipids, and thus respond differently to decontamination than enveloped viruses that carry away a part of the host membrane. . physical methods, such as steam or dry heat, autoclaving is the most practical method for most laboratories. autoclave.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which of the following does not kill endospores? A. autoclaving B. incineration C. hot-air sterilization D. pasteurization E. all of the above kill endospores, Which of the following is most effective for sterilizing mattresses and plastic Petri dishes? A. chlorine B. ethylene oxide C. glutaraldehyde D. autoclaving E. non .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like A sterile item is free of a) microbes, viruses, AND prions. b) all viable microbes, endospores, AND viruses c) endospores, viruses, AND prions. d) microbes, endospores, AND prions. e) prions only., A common application of dry heat in the microbiology laboratory is to a) prepare specimens for study. b) sterilize .
which of the following does not kill microbes but physically removes them. pasteurization. irradiation. microwaving. filtration. . the autoclave treatment may be monitored by. . (non-enveloped) c influenza virus (enveloped) d e. coli. Choose matching definition. a. e. c. b. Don't know? 29 of 45.inactivates lipids. c.does not affect non-enveloped viruses. d.is used in gaseous form. e. kills bacteria but does not affect endospores. and more. . bacterial growth. - it is very effective at the mechanical removal of microorganisms. - all soaps are virucidal and kill all viruses. - plain soap is bactericidal and kills all bacteria. - all .Why is autoclaving rather than boiling water used for sterilization? Autoclaving uses dry heat instead of water. Boiling water is too hot and may denature proteins. Boiling water does not kill everything, including bacterial endospores and some protozoan cysts. Autoclaving is much faster than boiling water.
non-enveloped (naked) virus. gram-negative bacteria. gram-positive bacteria. enveloped viruses . The shortest time required to kill or inactivate all the microbes at a specified temperature is called the . pasteurization. moist heat autoclave. chlorination. filtration. boiling water. 17 of 25. Term. Intermittent sterilization, which uses 3 .
Viruses: Despite their smaller size and different composition compared to bacteria, viral particles are also effectively inactivated by autoclaving. This includes enveloped viruses like HIV and non-enveloped viruses like norovirus, which are otherwise challenging to eradicate.
It effectively transfers heat to kill microorganisms. 17 of 105. Term. . What might happen if the autoclave does not reach the minimum temperature of 121°C during a sterilization cycle? . (non enveloped viruses) Loss of biological activity. Washing hands with soap and water. Preparing surgical instruments.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like One of the first chemicals used by Lister to prevent surgical sepsis was A. alcohol. B. iodine. C. carbolic acid. D. mercury., The process of killing or removing all the microorganisms in or on a material is termed A. sterilization. B. disinfection. C. sanitation. D. antisepsis., A sterile item is free of A. microbes.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Define the terms sterilization, disinfection, and antisepsis., Put the microorganisms in order from *hardest to easiest* to kill in most circumstances: Naked viruses, vegetative bacteria, enveloped viruses, Mycobacteria, endospores, fungi, High temperatures ________ and low temperatures typically ___________. .Select one: A. bacterial endospores B. enveloped viruses C. non-enveloped viruses D. vegetative bacteria a. bacterial endospores One problem with using ultraviolet radiation for disinfection is Select one: A. does not penetrate well B. does not affect .
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like 1) which of the following does not kill endospores? a) autoclaving b) incineration c) hot-air sterilization d) pasteurization e) all of the above kill endospores, 2)Which of the following is most effective for sterilizing mattresses and plastic petri dishes? a) chlorine b) ethylene oxide c) glutaraldehyde d) autoclaving e) non .The number of cells in a culture will most influence the _____ necessary to kill them. time. temperature. volume. pressure. . As the pressure in an autoclave increases, the boiling point of ___ also increases, as does the temperature at which ___ forms. . -protozoan cysts & oocysts -bacterial endospores-non-enveloped viruses-mycobacterium .
Quiz yourself with questions and answers for Chapt 5 test microbio, so you can be ready for test day. Explore quizzes and practice tests created by teachers and students or create one from your course material.Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Put the following microbes in order of their resistance to antimicrobial agents, from least to most resistant: a. prions b. enveloped viruses c. mycobacteria d. Gram-negative bacteria, Hydrogen peroxide is an example of a(n) __________ and can serve as an effective disinfectant, though it does NOT work well .Quiz yourself with questions and answers for Exam 2 Study guide (Part II), so you can be ready for test day. Explore quizzes and practice tests created by teachers and students or create one from your course material.1. Prions 2. endospores 3. gram negative bacteria 4. gram positive bacteria 5. enveloped virus While you might think that a viral envelope would confer protection, it is more easily broken down than a protein coat. Gram-positive bacteria tend to be more susceptible to agents that attack the cell wall (recall that they lack an outer membrane). Bacterial endospores are designed to .
elisa test gluten
E. is a process that uses short bursts of radiation to kill microorganisms on foods., _____ is a common environmental organism that may even grow in certain chemical disinfectants A. Escherichia coli. B.Influenza virus (enveloped). C.Streptococcus pneumoniae. D.Adenoviruses (non-enveloped).
The process that destroys or removes all viable microorganisms (including viruses) with the exception of prions Generally reserved for inanimate objects as it would be impractical or dangerous to sterilize parts of the human body Common uses: surgical instruments, syringes, commercially packaged food Heat (autoclave) Sterilants (chemical agents capable of .Endospores Vegetative fungi Large, non-enveloped viruses Small, non-enveloped viruses Mycobacteria Prions Enveloped viruses Gram positive bacteria Gram negative bacteria Fungal spores. 1. . How long does it take for an autoclave to kill all vegetative organisms and most endospores? 15 minutes. What three things should we know about ethylene .
Not effective against non-enveloped viruses, fungi, and bacterial spores; Area to be disinfected must be cleaned and rinsed free of soap; Low in cost; Phenolics. Includes O-phenophenoate-based Compounds; Effective against bacteria (especially gram-positive bacteria) and enveloped viruses; Not effective against nonenveloped viruses and spores
viruses with envelope on surface
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like What is the difference between an enveloped and non-enveloped virus?, What is the difference between lytic (virulent) and temperate (latent) phages?, When a bacterium is in a state of lysogenic conversion, why does it express a different protein(s)---often a toxin? What does this mean for the pathogenicity of the .Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like The thermal death time for a suspension of Bacillus subtilis endospores is 30 minutes in dry heat and less than 10 minutes in an autoclave. Which type of heat is more effective? Why?, If pasteurization does not achieve sterilization, why is pasteurization used to treat food?, Thermal death point is not considered .
viruses with envelope on skin
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Washing dishes in the dishwasher with detergent and hot water is a ________ process. A) antiseptic B) disinfecting C) sterilizing D) sanitizing E) degerming, Which of the following statements is TRUE of disinfectants? A) They are effective in destroying endospores. B) They are used on living tissue. C) They are .destroy vegetative bacteria, mycobacteria, fungi, and most viruses Disinfect non-critical instruments. Low-level disinfectants. destroy fungi, vegetative bacteria except mycobacteria, and enveloped viruses Do not kill endospores, naked viruses Disinfect furniture, . pipettes Applied in special chamber resembling autoclave Limitations: . Enveloped and non-enveloped viruses One of the major and best-known virus classifications is the separation of enveloped from non-enveloped viruses. In general, what distinguishes them is the presence (for enveloped viruses) or absence (for non-enveloped viruses) of a lipid bilayer membrane on the outer part of the virus.
viruses with envelope capsid
The Fedegari name is synonymous with technology, innovation and avant-garde design in the sterilization industry. Fedegari Autoklaven AG was established in Lugano in the early 1980's .
does autoclaving kill non-enveloped viruses|viruses with envelope on surface